In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy and traceability.
The outcome of the comparison can result in one of the following:
- no significant error being noted on the device under test
- a significant error being noted but no adjustment made
- an adjustment made to correct the error to an acceptable level
Strictly speaking, the term “calibration” means just the act of comparison and does not include any subsequent adjustment.
The calibration standard is normally traceable to a national standard held by a national metrological body.

SI | A concise summary of the International System of Units, SI
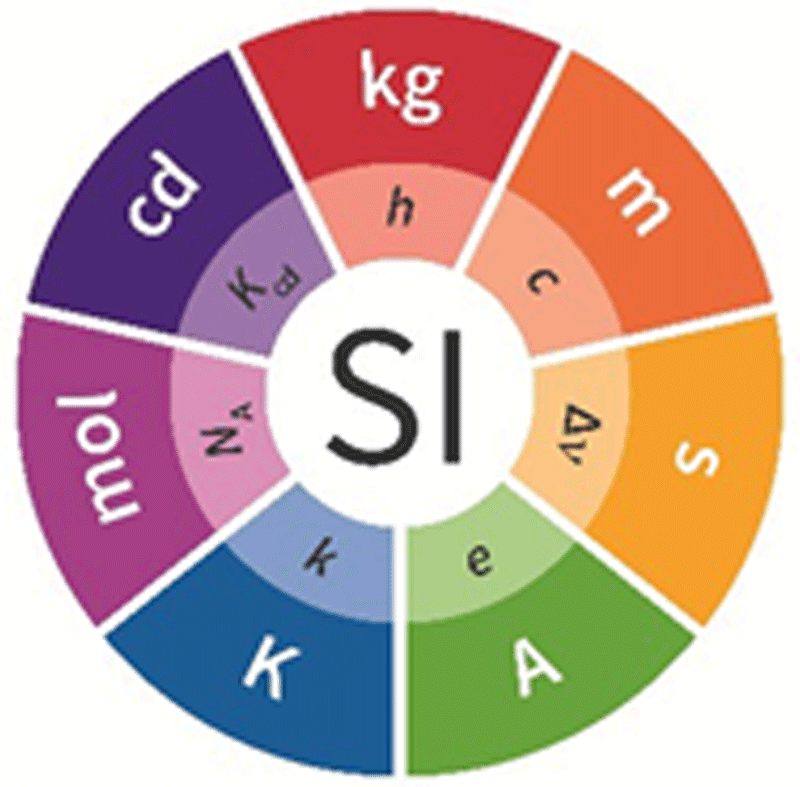
Metrology is the science of measurement and its application. Metrology includes all theoretical and practical aspects of measurement, whatever the measurement uncertainty and field of application.
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) was established by Article 1 of the Metre Convention, which was signed on 20 May 1875. It is charged with providing the basis for a single, coherent system of measurements to be used throughout the world and it operates under the authority of the International Committee of Weights and Measures (CIPM). The decimal metric system, dating from the time of the French Revolution, was based in 1799 on the metre and the kilogram. Under the terms of the Metre Convention, new international prototypes of the metre and kilogram were manufactured and formally adopted by the first General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1889. In 1960 the 11th CGPM formally defined and established the International System of Units (SI). Since then the SI has been periodically updated to take account of advances in science and the need for measurements in new domains. The last major revision was adopted by the 26th CGPM (2018), which decided that the SI would be based on the fixed numerical values of a set of seven defining constants from which the definitions of the seven base units of the SI would be deduced.